Python while循环语句
while循环语句在Python编程语言中,只要给定的条件为真时重复执行的目标语句。
语法:
在Python编程语言中while循环的语法是:
while expression: statement(s)
在这里,语句可以是单一语句或语句块。该条件可以是任何表达式,并且真正是任意非零值。循环迭代当条件为true。
当条件为假,则程序控制转到紧接在循环之后的一行。
在Python中,所有的程序代码结构通过缩进字符空格相同数量的语句被认为是一个单一的代码块的一部分。 Python使用缩进作为分组语句的方法。
流程图:
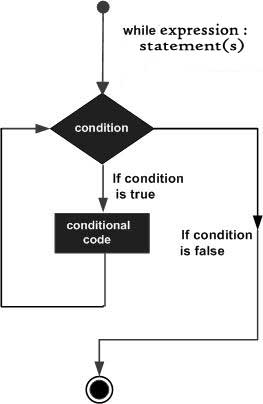
Here, key yiibai of the while loop is that the loop might not ever run. When the condition is tested and the result is false, the loop body will be skipped and the first statement after the while loop will be executed.
例子:
#!/usr/bin/python count = 0 while (count < 9): print 'The count is:', count count = count + 1 print "Good bye!"
When the above code is executed, it produces the following result:
The count is: 0 The count is: 1 The count is: 2 The count is: 3 The count is: 4 The count is: 5 The count is: 6 The count is: 7 The count is: 8 Good bye!
The block here, consisting of the print and increment statements, is executed repeatedly until count is no longer less than 9. With each iteration, the current value of the index count is displayed and then increased by 1.
The Infinite Loop:
A loop becomes infinite loop if a condition never becomes false. You must use caution when using while loops because of the possibility that this condition never resolves to a false value. This results in a loop that never ends. Such a loop is called an infinite loop.
An infinite loop might be useful in client/server programming where the server needs to run continuously so that client programs can communicate with it as and when required.
#!/usr/bin/python var = 1 while var == 1 : # This constructs an infinite loop num = raw_input("Enter a number :") print "You entered: ", num print "Good bye!"
When the above code is executed, it produces the following result:
Enter a number :20
You entered: 20
Enter a number :29
You entered: 29
Enter a number :3
You entered: 3
Enter a number between :Traceback (most recent call last):
File "test.py", line 5, in <module>
num = raw_input("Enter a number :")
KeyboardInterrupt
Above example will go in an infite loop and you would need to use CTRL+C to come out of the program.
The else Statement Used with Loops
Python supports to have an else statement associated with a loop statement.
-
If the else statement is used with a for loop, the else statement is executed when the loop has exhausted iterating the list.
-
If the else statement is used with a while loop, the else statement is executed when the condition becomes false.
The following example illustrates the combination of an else statement with a while statement that prints a number as long as it is less than 5, otherwise else statement gets executed.
#!/usr/bin/python count = 0 while count < 5: print count, " is less than 5" count = count + 1 else: print count, " is not less than 5"
When the above code is executed, it produces the following result:
0 is less than 5 1 is less than 5 2 is less than 5 3 is less than 5 4 is less than 5 5 is not less than 5
Single Statement Suites:
Similar to the if statement syntax, if your while clause consists only of a single statement, it may be placed on the same line as the while header.
Here is the syntax and example of a one-line while clause:
#!/usr/bin/python flag = 1 while (flag): print 'Given flag is really true!' print "Good bye!"
Its better not try above example because it will go into infinite loop and you will have to use CTRL+C keys to come out.

