Java异常处理
异常是一个问题的程序的执行期间产生了。异常可能会发生许多不同的原因,包括以下内容:
-
用户输入无效数据。
-
需要打开的文件不存在。
-
网络连接已丢失通信的中间或JVM已经耗尽内存。
有些例外的是由用户错误,其他人造成的程序员的错误,和其他人的失败以某种方式物理资源。
要了解在Java中如何异常处理工作,需要了解三类异常:
-
检查异常: 经过检查的异常是一个例外,通常是用户错误或不能由程序员不可预见的问题。例如,如果一个文件被打开,但该文件无法找到,则会出现异常。这些例外并不能简单地在编译时被忽略。
-
运行时异常: 运行时异常是发生,大概本来是可以避免程序员异常。而不是已检查异常,运行时异常是在编译时被忽略。
-
错误: 这些都不例外可言,但所出现超出用户或程序员的控制问题。错误通常忽略了你的代码,因为你可以很少做任何有关错误。例如,如果发生堆栈溢出时,会产生一个错误。他们还忽略了在编译的时候。
异常层次结构:
所有异常类是java.lang.Exception类的子类型。异常类是的Throwable类的子类。以外的异常类有另一个小类称为错误这是从Throwable的类中派生。
错误,一般都不会被困形成的Java程序。这些情况通常发生在出现严重故障,这不是由java程序处理。产生错误指示运行时环境中产生错误。例如:JVM是内存不足。通常的程序不能从错误中恢复。
Exception类主要有两个子类:IOException类和RuntimeException异常类。
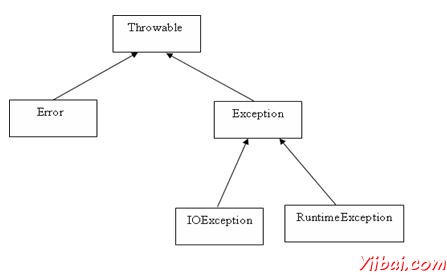
下面是最常见的选中和未选中列表 Java内置异常.
异常的方法:
以下是在Throwable类中提供重要的方法列表。
| SN | 方法及描述 |
|---|---|
| 1 |
public String getMessage() 返回有关已发生的异常的详细消息。此消息在Throwable的构造函数中初始化。 |
| 2 |
public Throwable getCause() 返回异常由一个Throwable对象所代表的原因。 |
| 3 |
public String toString() 返回类连接在一起的getMessage()结果的名称。 |
| 4 |
public void printStackTrace() 打印toString()结果以及堆栈跟踪到System.err,错误输出流的结果。 |
| 5 |
public StackTraceElement [] getStackTrace() 返回包含在堆栈跟踪每一个元素的数组。索引为0的元素表示的调用堆栈的顶部,并在阵列中的最后一个元素表示的方法在调用堆栈的底部。 |
| 6 |
public Throwable fillInStackTrace() 填补了这个Throwable对象的堆栈跟踪与当前的堆栈跟踪,增加在堆栈跟踪以前的任何信息。 |
捕获异常:
一种捕获的方法是使用try和catch关键字的组合异常。try/ catch块放在围绕之中,可能产生异常的代码。try/catch块中的代码被称为受保护的代码,以及语法使用try/catch语句如下所示:
try { //Protected code }catch(ExceptionName e1) { //Catch block }
catch语句涉及声明异常的正在试图捕捉类型。如果受保护的代码发生异常,catch块(或块)后面的试一下检查。如果发生异常的类型列在catch块,异常被传递到catch块多作为一个参数被传递到方法参数。
例子:
下面是一个数组并有2个元素声明。然后代码试图访问它抛出一个异常数组的第三个元素。
// File Name : ExcepTest.java import java.io.*; public class ExcepTest{ public static void main(String args[]){ try{ int a[] = new int[2]; System.out.println("Access element three :" + a[3]); }catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e){ System.out.println("Exception thrown :" + e); } System.out.println("Out of the block"); } }
这将产生以下结果:
Exception thrown :java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: 3 Out of the block
多个catch块:
一个try块后面可以跟多个catch块。多个catch代码块语法如下所示:
try { //Protected code }catch(ExceptionType1 e1) { //Catch block }catch(ExceptionType2 e2) { //Catch block }catch(ExceptionType3 e3) { //Catch block }
前面的语句演示3个catch块,但可以有任意数量的其中的一个try后。如果受保护的代码发生异常,该异常被抛出到列表中的第一个catch块。如果抛出的异常的数据类型相匹配ExceptionType1,它就会被捕获那里。如果不是,则该异常传递到第二catch语句. 这种情况持续下去,直到异常要么被捕获或下落通过全部捕获,在这种情况下,目前的方法停止执行并抛出异常下落到以前的方法调用堆栈。
例子:
下面是代码段展示了如何使用多个try/catch语句。
try { file = new FileInputStream(fileName); x = (byte) file.read(); }catch(IOException i) { i.printStackTrace(); return -1; }catch(FileNotFoundException f) //Not valid! { f.printStackTrace(); return -1; }
throws/throw 关键字:
如果一个方法不处理未处理异常,该方法必须使用throw关键字声明它。在抛出的关键字出现在方法签名的结束。
可以抛出一个异常,或者是一个新实例化刚刚捕获的异常,使用throw关键字。试着去了解不同的抛出异常和throw关键字。
下面的方法声明它会抛出一个RemoteException:
import java.io.*; public class className { public void deposit(double amount) throws RemoteException { // Method implementation throw new RemoteException(); } //Remainder of class definition }
一个方法可以声明它抛出多个异常,在这种情况下,异常都是在以逗号分隔的列表中声明。例如,下面的方法声明它会抛出一个RemoteException和InsufficientFundsException:
import java.io.*; public class className { public void withdraw(double amount) throws RemoteException, InsufficientFundsException { // Method implementation } //Remainder of class definition }
finally 关键字
finally关键字是用来创建一个代码块后面一个try块。 finally块中的代码总是执行,不论是否发生异常。
使用finally块可以运行要执行代码,不管在受保护的代码会发生什么,可用于清理工作类型语句。
finally块出现在catch块的结尾并具有以下语法:
try { //Protected code }catch(ExceptionType1 e1) { //Catch block }catch(ExceptionType2 e2) { //Catch block }catch(ExceptionType3 e3) { //Catch block }finally { //The finally block always executes. }
例子:
public class ExcepTest{ public static void main(String args[]){ int a[] = new int[2]; try{ System.out.println("Access element three :" + a[3]); }catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e){ System.out.println("Exception thrown :" + e); } finally{ a[0] = 6; System.out.println("First element value: " +a[0]); System.out.println("The finally statement is executed"); } } }
这将产生以下结果:
Exception thrown :java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: 3 First element value: 6 The finally statement is executed
请注意以下几点:
-
catch子句不可以不存在一个try语句。
-
它不是强制性的有finally子句时,总会有一个try / catch块存在。
-
try块中不能出现没有任何catch子句或finally子句。
-
任何代码不能出现在 try, catch, finally 块之间。
声明自己的异常:
可以在Java中创建自己的异常。编写自己的异常类时请注意以下几点:
-
所有的异常必须是Throwable的子类。
-
如果想写一个检查异常是处理自动执行或声明规则,需要扩展Exception类。
-
如果想编写一个运行时异常,则需要扩展RuntimeException类。
我们可以定义如下自己的异常处理类:
class MyException extends Exception{ }
只需要扩展Exception类来创建自己的异常类。这些被认为是已检查异常。下面InsufficientFundsException类是扩展了Exception类,使其成为检查的异常用户定义的异常。一个异常类是像任何其他类,包含有用的字段和方法。
例子:
// File Name InsufficientFundsException.java import java.io.*; public class InsufficientFundsException extends Exception { private double amount; public InsufficientFundsException(double amount) { this.amount = amount; } public double getAmount() { return amount; } }
为了证明我们的使用用户定义的异常,下面的CheckingAccount类包含一个withdraw() 方法抛出一个InsufficientFundsException。
// File Name CheckingAccount.java import java.io.*; public class CheckingAccount { private double balance; private int number; public CheckingAccount(int number) { this.number = number; } public void deposit(double amount) { balance += amount; } public void withdraw(double amount) throws InsufficientFundsException { if(amount <= balance) { balance -= amount; } else { double needs = amount - balance; throw new InsufficientFundsException(needs); } } public double getBalance() { return balance; } public int getNumber() { return number; } }
下面BankDemo程序演示调用deposit()和withdraw() 方法。
// File Name BankDemo.java public class BankDemo { public static void main(String [] args) { CheckingAccount c = new CheckingAccount(101); System.out.println("Depositing $500..."); c.deposit(500.00); try { System.out.println(" Withdrawing $100..."); c.withdraw(100.00); System.out.println(" Withdrawing $600..."); c.withdraw(600.00); }catch(InsufficientFundsException e) { System.out.println("Sorry, but you are short $" + e.getAmount()); e.printStackTrace(); } } }
编译所有上述三个文件并运行BankDemo,这将产生以下结果:
Depositing $500... Withdrawing $100... Withdrawing $600... Sorry, but you are short $200.0 InsufficientFundsException at CheckingAccount.withdraw(CheckingAccount.java:25) at BankDemo.main(BankDemo.java:13)
常见的异常:
在Java中,可以定义两类异常和错误。
-
JVM 异常: - 这些是完全或逻辑抛出由JVM异常/错误。例如:NullPointerException异常,ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException异常,抛出ClassCastException,
-
编程异常: - 这些异常是由应用程序或API编程实例明确地抛出,如:IllegalArgumentException, IllegalStateException.

