JOGL图形形状
本在线教程介绍了绘制直线,用直线的各种形状。 OpenGL的API提供了原始的方法,用这些方法,可以开发形状,如三角形,多边形和圆形绘制基本图形元素如点,顶点,线等。或者二维和三维。
图形对象
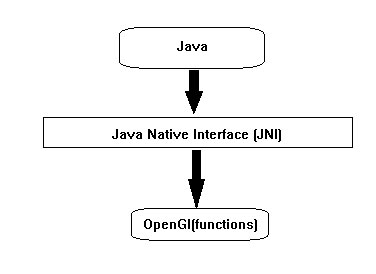
要访问程序特定于硬件和操作系统平台,以及其他语言编写,比如C和C++(原生应用)库,Java使用一种称为Java本地接口(JNI)编程框架的工作。 JOGL内部使用此接口,如图中下面的图表来访问OpenGL函数。
GLEventListener接口的所有四种方法让代码(Java JOGL方法),它内部调用OpenGL函数,这些JOGL方法的命名也类似于 OpenGL 命名约定。如果在OpenGL中的函数名是在glBegin(),它被用作gl.glBegin()。
只要gl.glBegin()的Java JOGL的方法被调用时,它在内部调用OpenGL的glBegin()方法。这是在安装JOGL的时间对用户的系统上安装本地库文件的原因。
Display() 方法
这是其中包含用于开发图形的代码的一个重要方法。这就要求GLAutoDrawable接口对象作为参数。
Display()方法中,首先得到使用GL接口的对象的OpenGL上下文(GL继承GLBase接口,该接口包含的方法来生成所有的OpenGL上下文对象)。由于本在线教程是关于JOGL2让我们产生GL2对象。
让我们通过代码片段获取GL2对象:
//Generating GL object GL gl=drawable.getGL(); GL gl=drawable.getGL(); //Using this Getting the Gl2 Object //this can be written in a single line like final GL2 gl = drawable.getGL().getGL2();
使用GL2接口的对象,就可以访问GL2接口的成员,而这又提供了访问 OpenGL[1.0 ...3.0]功能。
绘制一条线
GL2接口包含的方法和列表,但这里的三个主要方法的重要论述,即函数是glBegin()glVertex()和glEnd()。
| Sr. No. | 方法及描述 |
|---|---|
| 1 |
glBegin() 此方法开始画线过程。它采用预定义的字符串整数“GL_LINES”作为一个参数,它是由GL接口继承。 |
| 2 |
glVertex3f()/glVertex2f() 此方法创建的顶点,我们必须通过坐标参数3f 和 2f,,这表示3维的浮点坐标和2维浮点分别坐标。 |
| 3 |
glEnd() 行结尾 |
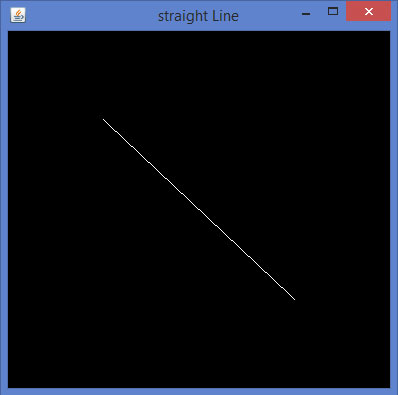
让我们通过程序来绘制一条直线:
import javax.media.opengl.GL2; import javax.media.opengl.GLAutoDrawable; import javax.media.opengl.GLCapabilities; import javax.media.opengl.GLEventListener; import javax.media.opengl.GLProfile; import javax.media.opengl.awt.GLCanvas; import javax.swing.JFrame; public class Line implements GLEventListener{ @Override public void display(GLAutoDrawable drawable) { final GL2 gl = drawable.getGL().getGL2(); gl.glBegin (GL2.GL_LINES);//static field gl.glVertex3f(0.50f,-0.50f,0); gl.glVertex3f(-0.50f,0.50f,0); gl.glEnd(); } @Override public void dispose(GLAutoDrawable arg0) { //method body } @Override public void init(GLAutoDrawable arg0) { // method body } @Override public void reshape(GLAutoDrawable arg0, int arg1, int arg2, int arg3, int arg4) { // method body } public static void main(String[] args) { //getting the capabilities object of GL2 profile final GLProfile profile = GLProfile.get(GLProfile.GL2); GLCapabilities capabilities = new GLCapabilities(profile); // The canvas final GLCanvas glcanvas = new GLCanvas(capabilities); Line l = new Line(); glcanvas.addGLEventListener(l); glcanvas.setSize(400, 400); //creating frame final JFrame frame = new JFrame ("straight Line"); //adding canvas to frame frame.getContentPane().add(glcanvas); frame.setSize(frame.getContentPane().getPreferredSize()); frame.setVisible(true); }//end of main }//end of classimport javax.media.opengl.GL2;
使用GL_LINES绘制形状
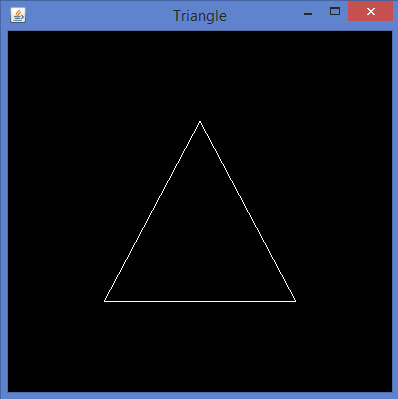
让我们通过一个程序使用GL_LINES绘制一个三角形:
import javax.media.opengl.GL2; import javax.media.opengl.GLAutoDrawable; import javax.media.opengl.GLCapabilities; import javax.media.opengl.GLEventListener; import javax.media.opengl.GLProfile; import javax.media.opengl.awt.GLCanvas; import javax.swing.JFrame; public class Triangle implements GLEventListener{ @Override public void display(GLAutoDrawable drawable) { final GL2 gl = drawable.getGL().getGL2(); gl.glBegin (GL2.GL_LINES); //drawing the base gl.glBegin (GL2.GL_LINES); gl.glVertex3f(-0.50f, -0.50f, 0); gl.glVertex3f(0.50f, -0.50f, 0); gl.glEnd(); //drawing the right edge gl.glBegin (GL2.GL_LINES); gl.glVertex3f(0f, 0.50f, 0); gl.glVertex3f(-0.50f, -0.50f, 0); gl.glEnd(); //drawing the lft edge gl.glBegin (GL2.GL_LINES); gl.glVertex3f(0f, 0.50f, 0); gl.glVertex3f(0.50f, -0.50f, 0); gl.glEnd(); gl.glFlush(); } @Override public void dispose(GLAutoDrawable arg0) { //method body } @Override public void init(GLAutoDrawable arg0) { // method body } @Override public void reshape(GLAutoDrawable arg0, int arg1, int arg2, int arg3, int arg4) { // method body } public static void main(String[] args) { //getting the capabilities object of GL2 profile final GLProfile profile = GLProfile.get(GLProfile.GL2); GLCapabilities capabilities = new GLCapabilities(profile); // The canvas final GLCanvas glcanvas = new GLCanvas(capabilities); Triangle l = new Triangle(); glcanvas.addGLEventListener(l); glcanvas.setSize(400, 400); //creating frame final JFrame frame = new JFrame ("Triangle"); //adding canvas to frame frame.getContentPane().add(glcanvas); frame.setSize(frame.getContentPane().getPreferredSize()); frame.setVisible(true); }//end of main }//end of classimport javax.media.opengl.GL2;
如果编译并执行上述程序,将生成以下输出。它示出了使用glBegin()方法的GL_LINES画出一个三角形。
让我们通过一个程序中使用GL_LINES画一个菱形:
import javax.media.opengl.GL2; import javax.media.opengl.GLAutoDrawable; import javax.media.opengl.GLCapabilities; import javax.media.opengl.GLEventListener; import javax.media.opengl.GLProfile; import javax.media.opengl.awt.GLCanvas; import javax.swing.JFrame; public class Rhombus implements GLEventListener{ @Override public void display( GLAutoDrawable drawable ) { final GL2 gl = drawable.getGL().getGL2(); //edge1 gl.glBegin( GL2.GL_LINES ); gl.glVertex3f( 0.0f,0.75f,0 ); gl.glVertex3f( -0.75f,0f,0 ); gl.glEnd(); //edge2 gl.glBegin( GL2.GL_LINES ); gl.glVertex3f( -0.75f,0f,0 ); gl.glVertex3f( 0f,-0.75f, 0 ); gl.glEnd(); //edge3 gl.glBegin( GL2.GL_LINES ); gl.glVertex3f( 0f,-0.75f, 0 ); gl.glVertex3f( 0.75f,0f, 0 ); gl.glEnd(); //edge4 gl.glBegin( GL2.GL_LINES ); gl.glVertex3f( 0.75f,0f, 0 ); gl.glVertex3f( 0.0f,0.75f,0 ); gl.glEnd(); gl.glFlush(); } @Override public void dispose( GLAutoDrawable arg0 ) { //method body } @Override public void init(GLAutoDrawable arg0 ) { // method body } @Override public void reshape( GLAutoDrawable arg0, int arg1, int arg2, int arg3, int arg4 ) { // method body } public static void main( String[] args ) { //getting the capabilities object of GL2 profile final GLProfile profile = GLProfile.get( GLProfile.GL2 ); GLCapabilities capabilities = new GLCapabilities( profile ); // The canvas final GLCanvas glcanvas = new GLCanvas( capabilities ); Rhombus rhombus = new Rhombus(); glcanvas.addGLEventListener( rhombus ); glcanvas.setSize( 400, 400 ); //creating frame final JFrame frame = new JFrame ( "Rhombus" ); //adding canvas to frame frame.getContentPane().add( glcanvas ); frame.setSize( frame.getContentPane().getPreferredSize() ); frame.setVisible( true ); }//end of main }//end of class
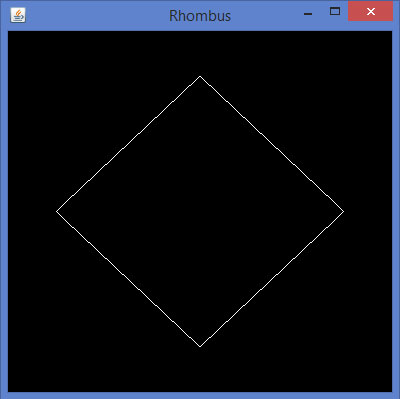
如果编译并执行以上程序,会得到下面的输出。它示出了使用在glBegin()方法的GL_LINES产生一个菱形。
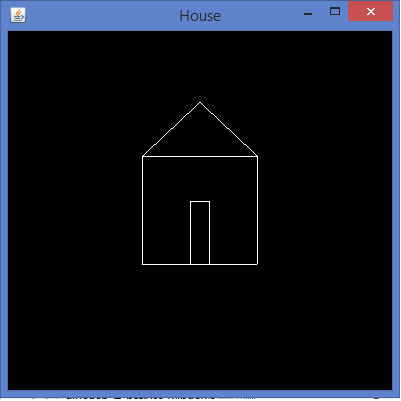
让我们通过一个程序使用GL_LINES画一所房子:
import javax.media.opengl.GL2; import javax.media.opengl.GLAutoDrawable; import javax.media.opengl.GLCapabilities; import javax.media.opengl.GLEventListener; import javax.media.opengl.GLProfile; import javax.media.opengl.awt.GLCanvas; import javax.swing.JFrame; public class House implements GLEventListener{ @Override public void display( GLAutoDrawable drawable ) { final GL2 gl = drawable.getGL().getGL2(); //drawing top gl.glBegin ( GL2.GL_LINES ); gl.glVertex3f( -0.3f, 0.3f, 0 ); gl.glVertex3f( 0.3f,0.3f, 0 ); gl.glEnd(); //drawing bottom gl.glBegin( GL2.GL_LINES ); gl.glVertex3f( -0.3f,-0.3f, 0 ); gl.glVertex3f( 0.3f,-0.3f, 0 ); gl.glEnd(); //drawing the right edge gl.glBegin( GL2.GL_LINES ); gl.glVertex3f( -0.3f,0.3f, 0 ); gl.glVertex3f( -0.3f,-0.3f, 0 ); gl.glEnd(); //drawing the left edge gl.glBegin( GL2.GL_LINES ); gl.glVertex3f( 0.3f,0.3f,0 ); gl.glVertex3f( 0.3f,-0.3f,0 ); gl.glEnd(); //building roof //building lft dia gl.glBegin( GL2.GL_LINES ); gl.glVertex3f( 0f,0.6f, 0 ); gl.glVertex3f( -0.3f,0.3f, 0 ); gl.glEnd(); //building rt dia gl.glBegin( GL2.GL_LINES ); gl.glVertex3f( 0f,0.6f, 0 ); gl.glVertex3f( 0.3f,0.3f, 0 ); gl.glEnd(); //building door //drawing top gl.glBegin ( GL2.GL_LINES ); gl.glVertex3f( -0.05f, 0.05f, 0 ); gl.glVertex3f( 0.05f, 0.05f, 0 ); gl.glEnd(); //drawing the left edge gl.glBegin ( GL2.GL_LINES ); gl.glVertex3f( -0.05f, 0.05f, 0 ); gl.glVertex3f( -0.05f, -0.3f, 0 ); gl.glEnd(); //drawing the right edge gl.glBegin ( GL2.GL_LINES ); gl.glVertex3f( 0.05f, 0.05f, 0 ); gl.glVertex3f( 0.05f, -0.3f, 0 ); gl.glEnd(); } @Override public void dispose( GLAutoDrawable arg0 ) { //method body } @Override public void init( GLAutoDrawable arg0 ) { // method body } @Override public void reshape( GLAutoDrawable arg0, int arg1, int arg2, int arg3, int arg4 ) { // method body } public static void main( String[] args ) { //getting the capabilities object of GL2 profile final GLProfile profile = GLProfile.get( GLProfile.GL2 ); GLCapabilities capabilities = new GLCapabilities( profile ); // The canvas final GLCanvas glcanvas = new GLCanvas( capabilities ); House house = new House(); glcanvas.addGLEventListener( house ); glcanvas.setSize(400, 400); //creating frame final JFrame frame = new JFrame( "House" ); //adding canvas to frame frame.getContentPane().add( glcanvas ); frame.setSize( frame.getContentPane().getPreferredSize() ); frame.setVisible( true ); }//end of main }//end of class
如果编译并执行以上程序,会得到下面的输出。它示出了使用GL_LINES()方法生成一所房子的图。
使用glBegin()更多的参数绘画出更多的形状
除了GL_LINES预定义的字符串参数,glBegin()方法接受八个参数。可以用它来绘制不同的形状。这些用于相同GL_LINES。
下表显示了glBegin()方法的参数和描述:
| Sr. No. | 参数和描述 |
|---|---|
| 1 |
GL_LINES 创建每对顶点作为一个独立的线段。 |
| 2 |
GL_LINE_STRIP 绘制线段的连接组从第一顶点到最后。 |
| 3 |
GL_LINE_LOOP 绘制线段的从第一顶点到最后一个连接组再次回到第一个点。 |
| 4 |
GL_TRIANGLES 把顶点的每一三元组作为一个独立的三角形。 |
| 5 |
GL_TRIANGLE_STRIP 绘制三角形的连接组。一个三角形被定义为所述第一两个顶点后呈现的每个顶点。 |
| 6 |
GL_TRIANGLE_FAN 绘制三角形的连接组。一个三角形被定义为所述第一两个顶点后呈现的每个顶点。 |
| 7 |
GL_QUADS 将每个组的四个顶点作为一个独立的四边形。 |
| 8 |
GL_QUAD_STRIP 绘制四边形的连接组。一个四边形被定义为每对所述第一对后呈现的顶点。 |
| 9 |
GL_POLYGON 绘制一个单一的,凸多边形。顶点1,...,N定义这个多边形。 |
让我们来看看使用glBegin()参数的一些例子。
程序画线带钢:
import javax.media.opengl.GL2; import javax.media.opengl.GLAutoDrawable; import javax.media.opengl.GLCapabilities; import javax.media.opengl.GLEventListener; import javax.media.opengl.GLProfile; import javax.media.opengl.awt.GLCanvas; import javax.swing.JFrame; public class LineStrip implements GLEventListener{ @Override public void display(GLAutoDrawable drawable) { final GL2 gl = drawable.getGL().getGL2(); gl.glBegin (GL2.GL_LINE_STRIP); gl.glVertex3f(-0.50f,-0.75f, 0); gl.glVertex3f(0.7f,0.5f, 0); gl.glVertex3f(0.70f,-0.70f, 0); gl.glVertex3f(0f,0.5f, 0); gl.glEnd(); } @Override public void dispose(GLAutoDrawable arg0) { //method body } @Override public void init(GLAutoDrawable arg0) { // method body } @Override public void reshape(GLAutoDrawable arg0, int arg1, int arg2, int arg3, int arg4) { // method body } public static void main(String[] args) { //getting the capabilities object of GL2 profile final GLProfile profile = GLProfile.get(GLProfile.GL2); GLCapabilities capabilities = new GLCapabilities(profile); // The canvas final GLCanvas glcanvas = new GLCanvas(capabilities); LineStrip r = new LineStrip(); glcanvas.addGLEventListener(r); glcanvas.setSize(400, 400); //creating frame final JFrame frame = new JFrame ("LineStrip"); //adding canvas to frame frame.getContentPane().add(glcanvas); frame.setSize(frame.getContentPane().getPreferredSize()); frame.setVisible(true); }//end of main }//end of classimport javax.media.opengl.GL2;
如果编译并执行上面的代码,生成以下输出:
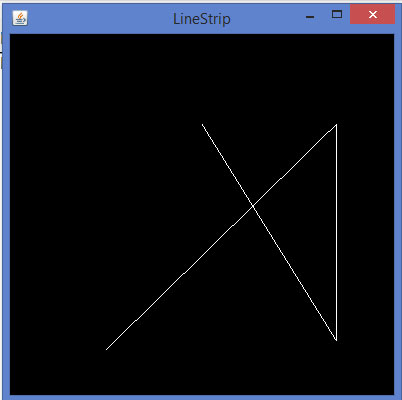
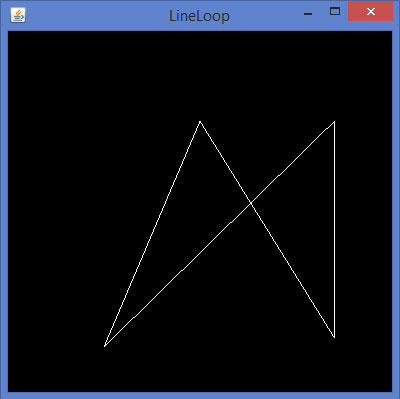
代码片段display()方法来绘制线路回路:
public void display(GLAutoDrawable drawable) { final GL2 gl = drawable.getGL().getGL2(); gl.glBegin (GL2.GL_LINE_LOOP); gl.glVertex3f( -0.50f, -0.75f, 0); gl.glVertex3f(0.7f, .5f, 0); gl.glVertex3f(0.70f, -0.70f, 0); gl.glVertex3f(0f, 0.5f, 0); gl.glEnd(); }
如果用上面的代码替换任何基本的模板方案的display()方法,编译并执行它,下面的输出生成:
代码片段display()方法使用GL_TRIANGLES画三角形
public void display(GLAutoDrawable drawable) { final GL2 gl = drawable.getGL().getGL2(); gl.glBegin(GL2.GL_TRIANGLES); // Drawing Using Triangles gl.glVertex3f(0.5f,0.7f,0.0f); // Top gl.glVertex3f(-0.2f,-0.50f,0.0f); // Bottom Left gl.glVertex3f(0.5f,-0.5f,0.0f); //Bottom Right gl.glEnd(); }
如果用上面的代码替换显示任何基本的模板程序的方法,编译并执行它,下面的输出生成:
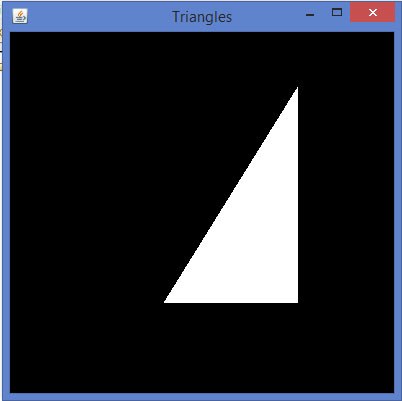
代码片段display()方法来绘制三角形:
public void display(GLAutoDrawable drawable) { final GL2 gl = drawable.getGL().getGL2(); gl.glBegin (GL2.GL_TRIANGLE_STRIP); gl.glVertex3f(0f,0.5f,0); gl.glVertex3f(-0.50f,-0.75f,0); gl.glVertex3f(0.28f,0.06f,0); gl.glVertex3f(0.7f,0.5f,0); gl.glVertex3f(0.7f,-0.7f,0); gl.glEnd(); }
如果要更换显示器的任何与上面的代码的基本模板方案的方法,编译并执行它,下面的输出生成:

代码片段display()方法来绘制四边形:
public void display(GLAutoDrawable drawable) { final GL2 gl = drawable.getGL().getGL2(); gl.glBegin(GL2.GL_QUADS); gl.glVertex3f( 0.0f,0.75f,0); gl.glVertex3f(-0.75f,0f,0); gl.glVertex3f(0f,-0.75f,0); gl.glVertex3f(0.75f,0f,0); gl.glEnd(); }
如果用上面的代码替换显示任何基本的模板程序的方法,编译并执行它,下面的输出生成:
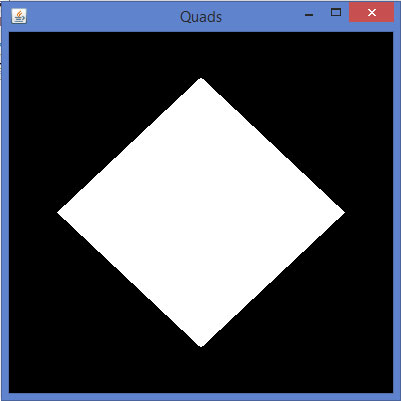
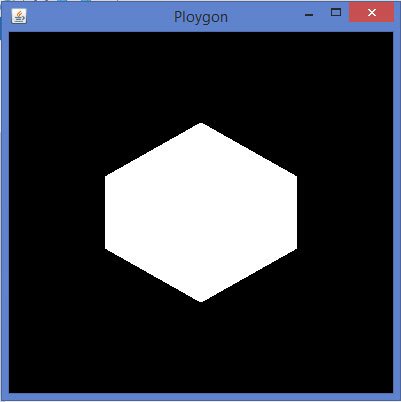
代码片段display()方法来绘制多边形:
public void display(GLAutoDrawable drawable) { final GL2 gl = drawable.getGL().getGL2(); gl.glBegin(GL2.GL_POLYGON); gl.glVertex3f(0f,0.5f,0f); gl.glVertex3f(-0.5f,0.2f,0f); gl.glVertex3f(-0.5f,-0.2f,0f); gl.glVertex3f(0f,-0.5f,0f); gl.glVertex3f(0f,0.5f,0f); gl.glVertex3f(0.5f,0.2f,0f); gl.glVertex3f(0.5f,-0.2f,0f); gl.glVertex3f(0f,-0.5f,0f); gl.glEnd(); }
如果用上面的代码替换任何基本的模板方案的display()方法,编译并执行它,会生成以下输出