Android内容提供者
内容提供程序(Provider)组件从一个应用到其他请求提供数据。通过 ContentResolver 类的方法这样的请求处理。内容提供程序使用不同的方式来存储数据,并且可以将数据存储在数据库中,文件中,甚至在网络上。
每一个 Android 应用程序运行在自己的进程保持一个应用程序数据,在另外一个应用程序中隐藏自己的权限。但有时需要在应用程序之间共享数据。这时内容提供程序是非常有用。
内容提供程序将内容集中在一个地方,让许多不同的应用访问。内容提供程序的行非常像数据库,可以对它进行查询,编辑等操作,添加或删除可使用 insert(), update(), delete(), query() 方法。在大多数情况下,这些数据都存储在SQlite数据库。
内容提供程序实施 ContentProvider 类的子类,必须实现了一套标准的 API,使其他应用程序来执行事务。
public class MyContentProvider extends ContentProvider { }
内容的URI
要查询内容提供程序,可以指定 URI 形式如以下格式的查询字符串:
<prefix>://<authority>/<data_type>/<id>
这里是URI的各个部分的细节
| 部分 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| prefix | 始终设置内容为 :// |
| authority | 规定内容提供商的名称,例如联系人,浏览器等。对于第三方内容提供商,这可能是完全合格的名称,如 com.yiibai.statusprovider |
| data_type | 表示数据,特定提供程序提供的类型。例如,如果得到所有的联系人的通讯录内容提供程序,那么数据路径URI是这样的 content://contacts/people |
| id | 规定要求的特定记录。例如,如果正在寻找联系人编号为5,在联系人内容提供者中,则URI是这样的 content://contacts/people/5. |
创建内容提供者
以下是简单的步骤用来创建自己的内容提供者的数量。
-
首先,需要创建一个内容提供者扩展 ContentProvider 基类。
-
其次,需要定义内容提供者用于访问内容的 URI 地址。
-
接下来,需要创建自己的数据库用于保存内容。通常情况下,Android使用SQLite数据库,并且框架需要重写 onCreate() 方法会使用 SQLite开放的 Helper方法来创建或打开提供者数据库。当启动应用程序时,每个内容提供者的onCreate()方法调用处理程序在主应用程序。
-
接下来,必须实现内容提供者查询来执行不同的数据库的具体操作。
-
最后,在activity文件使用<provider>标签注册内容提供者。
下面是需要覆盖内容提供程序类的方法的列表:
-
onCreate() 方法被称为提供者开始。
-
query() 方法接收来自客户端的请求。返回的结果作为一个Cursor对象。
-
insert() 方法插入一条新记录到内容提供者。
-
delete() 方法从内容提供者删除记录。
-
update() 方法从内容提供者更新现有记录。
-
getType() 此方法在给定的URI返回 MIME 类型的数据。
示例
这个例子将解释如何创建自己的 ContentProvider。因此按照下面的步骤类似于我们之前创建Hello World范例:
| Step | 描述 |
|---|---|
| 1 | 使用Eclipse IDE创建Android应用程序,并将它命名为MyContentProviderunder在包com.example.mycontentprovider下并使用空的Activity。 |
| 2 | 修改主要活动文件MainActivity.java增加两个新的方法onClickAddName() 和 onClickRetrieveStudents()。 |
| 3 | 创建一个新的名为StudentsProvider.java的java文件在packagecom.example.mycontentprovider包下,并定义实际提供者和相关方法。 |
| 4 | 使用注册内容提供者在AndroidManifest.xml文件中的<provider.../>标签 |
| 5 | 修改res/layout/activity_main.xml文件的默认内容包括一个小的GUI添加学生记录。 |
| 6 | 在res/values/strings.xml文件中定义所需的常量 |
| 7 | 运行该应用程序启动Android模拟器和验证应用程序所做的修改结果。 |
以下是主活动文件 src/com.example.mycontentprovider/MainActivity.java 修改后的内容。这个文件可以包括每个生命周期方法。我们已经增加了两个新方法onClickAddName() 和 onClickRetrieveStudents() 来处理用户与应用程序交互。
package com.example.mycontentprovider; import android.net.Uri; import android.os.Bundle; import android.app.Activity; import android.content.ContentValues; import android.content.CursorLoader; import android.database.Cursor; import android.view.Menu; import android.view.View; import android.widget.EditText; import android.widget.Toast; public class MainActivity extends Activity { @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); } @Override public boolean onCreateOptionsMenu(Menu menu) { getMenuInflater().inflate(R.menu.main, menu); return true; } public void onClickAddName(View view) { // Add a new student record ContentValues values = new ContentValues(); values.put(StudentsProvider.NAME, ((EditText)findViewById(R.id.txtName)).getText().toString()); values.put(StudentsProvider.GRADE, ((EditText)findViewById(R.id.txtGrade)).getText().toString()); Uri uri = getContentResolver().insert( StudentsProvider.CONTENT_URI, values); Toast.makeText(getBaseContext(), uri.toString(), Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show(); } public void onClickRetrieveStudents(View view) { // Retrieve student records String URL = "content://com.example.provider.College/students"; Uri students = Uri.parse(URL); Cursor c = managedQuery(students, null, null, null, "name"); if (c.moveToFirst()) { do{ Toast.makeText(this, c.getString(c.getColumnIndex(StudentsProvider._ID)) + ", " + c.getString(c.getColumnIndex( StudentsProvider.NAME)) + ", " + c.getString(c.getColumnIndex( StudentsProvider.GRADE)), Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show(); } while (c.moveToNext()); } } }
在 com.example.mycontentprovider 包下创建新的 StudentsProvider.java 文件,以下是内容:
package com.example.mycontentprovider; import java.util.HashMap; import android.content.ContentProvider; import android.content.ContentUris; import android.content.ContentValues; import android.content.Context; import android.content.UriMatcher; import android.database.Cursor; import android.database.SQLException; import android.database.sqlite.SQLiteDatabase; import android.database.sqlite.SQLiteOpenHelper; import android.database.sqlite.SQLiteQueryBuilder; import android.net.Uri; import android.text.TextUtils; public class StudentsProvider extends ContentProvider { static final String PROVIDER_NAME = "com.example.provider.College"; static final String URL = "content://" + PROVIDER_NAME + "/students"; static final Uri CONTENT_URI = Uri.parse(URL); static final String _ID = "_id"; static final String NAME = "name"; static final String GRADE = "grade"; private static HashMap<String, String> STUDENTS_PROJECTION_MAP; static final int STUDENTS = 1; static final int STUDENT_ID = 2; static final UriMatcher uriMatcher; static{ uriMatcher = new UriMatcher(UriMatcher.NO_MATCH); uriMatcher.addURI(PROVIDER_NAME, "students", STUDENTS); uriMatcher.addURI(PROVIDER_NAME, "students/#", STUDENT_ID); } /** * Database specific constant declarations */ private SQLiteDatabase db; static final String DATABASE_NAME = "College"; static final String STUDENTS_TABLE_NAME = "students"; static final int DATABASE_VERSION = 1; static final String CREATE_DB_TABLE = " CREATE TABLE " + STUDENTS_TABLE_NAME + " (_id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT, " + " name TEXT NOT NULL, " + " grade TEXT NOT NULL);"; /** * Helper class that actually creates and manages * the provider's underlying data repository. */ private static class DatabaseHelper extends SQLiteOpenHelper { DatabaseHelper(Context context){ super(context, DATABASE_NAME, null, DATABASE_VERSION); } @Override public void onCreate(SQLiteDatabase db) { db.execSQL(CREATE_DB_TABLE); } @Override public void onUpgrade(SQLiteDatabase db, int oldVersion, int newVersion) { db.execSQL("DROP TABLE IF EXISTS " + STUDENTS_TABLE_NAME); onCreate(db); } } @Override public boolean onCreate() { Context context = getContext(); DatabaseHelper dbHelper = new DatabaseHelper(context); /** * Create a write able database which will trigger its * creation if it doesn't already exist. */ db = dbHelper.getWritableDatabase(); return (db == null)? false:true; } @Override public Uri insert(Uri uri, ContentValues values) { /** * Add a new student record */ long rowID = db.insert( STUDENTS_TABLE_NAME, "", values); /** * If record is added successfully */ if (rowID > 0) { Uri _uri = ContentUris.withAppendedId(CONTENT_URI, rowID); getContext().getContentResolver().notifyChange(_uri, null); return _uri; } throw new SQLException("Failed to add a record into " + uri); } @Override public Cursor query(Uri uri, String[] projection, String selection, String[] selectionArgs, String sortOrder) { SQLiteQueryBuilder qb = new SQLiteQueryBuilder(); qb.setTables(STUDENTS_TABLE_NAME); switch (uriMatcher.match(uri)) { case STUDENTS: qb.setProjectionMap(STUDENTS_PROJECTION_MAP); break; case STUDENT_ID: qb.appendWhere( _ID + "=" + uri.getPathSegments().get(1)); break; default: throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unknown URI " + uri); } if (sortOrder == null || sortOrder == ""){ /** * By default sort on student names */ sortOrder = NAME; } Cursor c = qb.query(db, projection, selection, selectionArgs, null, null, sortOrder); /** * register to watch a content URI for changes */ c.setNotificationUri(getContext().getContentResolver(), uri); return c; } @Override public int delete(Uri uri, String selection, String[] selectionArgs) { int count = 0; switch (uriMatcher.match(uri)){ case STUDENTS: count = db.delete(STUDENTS_TABLE_NAME, selection, selectionArgs); break; case STUDENT_ID: String id = uri.getPathSegments().get(1); count = db.delete( STUDENTS_TABLE_NAME, _ID + " = " + id + (!TextUtils.isEmpty(selection) ? " AND (" + selection + ')' : ""), selectionArgs); break; default: throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unknown URI " + uri); } getContext().getContentResolver().notifyChange(uri, null); return count; } @Override public int update(Uri uri, ContentValues values, String selection, String[] selectionArgs) { int count = 0; switch (uriMatcher.match(uri)){ case STUDENTS: count = db.update(STUDENTS_TABLE_NAME, values, selection, selectionArgs); break; case STUDENT_ID: count = db.update(STUDENTS_TABLE_NAME, values, _ID + " = " + uri.getPathSegments().get(1) + (!TextUtils.isEmpty(selection) ? " AND (" + selection + ')' : ""), selectionArgs); break; default: throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unknown URI " + uri ); } getContext().getContentResolver().notifyChange(uri, null); return count; } @Override public String getType(Uri uri) { switch (uriMatcher.match(uri)){ /** * Get all student records */ case STUDENTS: return "vnd.android.cursor.dir/vnd.example.students"; /** * Get a particular student */ case STUDENT_ID: return "vnd.android.cursor.item/vnd.example.students"; default: throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unsupported URI: " + uri); } } }
以下将 AndroidManifest.xml 文件的内容修改。在这里添加了<provider.../>标签,包括内容提供者:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" package="com.example.mycontentprovider" android:versionCode="1" android:versionName="1.0" > <uses-sdk android:minSdkVersion="8" android:targetSdkVersion="17" /> <application android:allowBackup="true" android:icon="@drawable/ic_launcher" android:label="@string/app_name" android:theme="@style/AppTheme" > <activity android:name="com.example.mycontentprovider.MainActivity" android:label="@string/app_name" > <intent-filter> <action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" /> <category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" /> </intent-filter> </activity> <provider android:name="StudentsProvider" android:authorities="com.example.provider.College"> </provider> </application> </manifest>
以下将 res/layout/activity_main.xml 文件的内容包括一个按钮来自定义广播意图:
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent" android:orientation="vertical" > <TextView android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="Name" /> <EditText android:id="@+id/txtName" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_width="fill_parent" /> <TextView android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="Grade" /> <EditText android:id="@+id/txtGrade" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_width="fill_parent" /> <Button android:text="Add Name" android:id="@+id/btnAdd" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:onClick="onClickAddName" /> <Button android:text="Retrieve Students" android:id="@+id/btnRetrieve" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:onClick="onClickRetrieveStudents" /> </LinearLayout>
确保 res/values/strings.xml 文件有以下内容:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <resources> <string name="app_name">MyContentProvider</string> <string name="action_settings">Settings</string> <string name="hello_world">Hello world!</string> </resources>;
现在运行刚刚创建的应用程序 MyContentProvider。假设设置AVD并且已经做好了环境设置。要从Eclipse运行的应用程序,从工具栏打开一个项目的活动文件,并单击“Run”  图标。Eclipse AVD 安装的应用程序后并启动它,如果设置和应用程序没有问题,它会启动显示仿真器窗口(要耐心,可能有点慢,由你计算机的速度决定):
图标。Eclipse AVD 安装的应用程序后并启动它,如果设置和应用程序没有问题,它会启动显示仿真器窗口(要耐心,可能有点慢,由你计算机的速度决定):
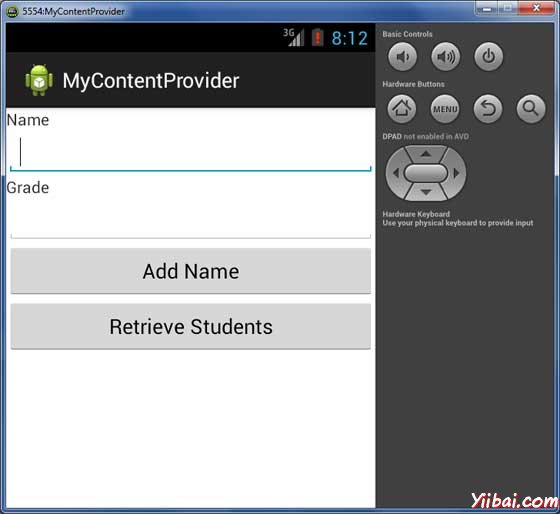
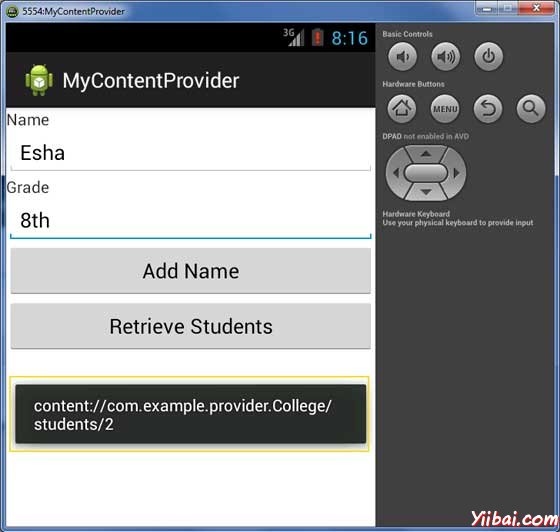
现在输入学生姓名和年级,最后单击“Add Name”按钮,将增加学生记录到数据库中,ContentProvider URI也一起添加到数据库中,底部显示的记录数,并会闪烁一条消息。此操作使得我们的insert()方法的使用。让我们重复这个过程,我们的内容提供者在数据库中添加一些更多的学生信息。
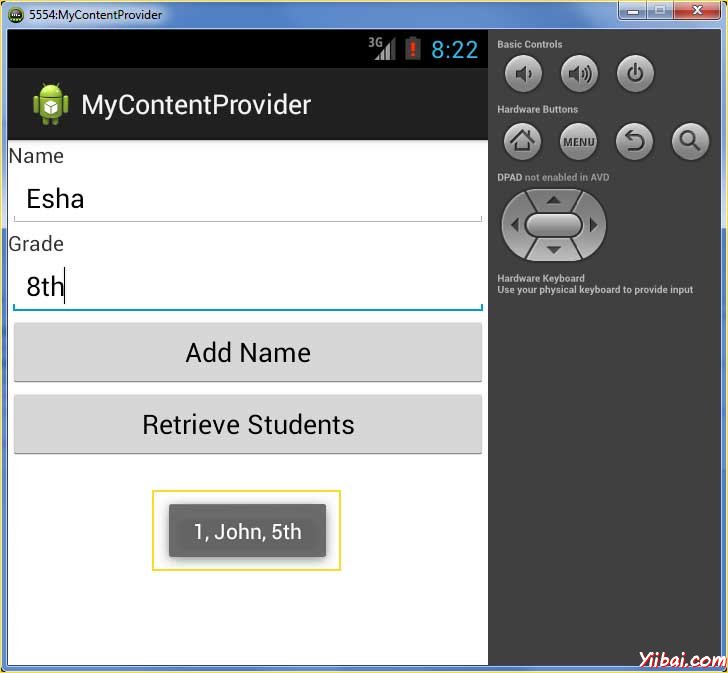
正在添加记录在数据库中,现在其时间让ContentProvider来给我们这些记录回,所以让我们的单击检索学生按钮,这将获取并显示所有记录这是按照我们执行query()方法。
可以编写活动 MainActivity.java文件提供的回调函数,然后修改用户界面,更新和删除操作按钮添加和读操作以同样的方式,因为我们已经做了更新和删除操作。
通过这种方式,可以使用现有的内容提供者,如地址簿,或不错的面向数据库应用开发,可以使用内容提供者的概念,可以执行所有的数据库操作,如排序读,写,更新和删除上面的例子中解释。

